What is a rotor? A rotor is a mechanical component that rotates around an axle. Essentially, it is the heart of many machines and engines. Rotors are components that have a critical role in the transfer and conversion of motion and energy.
What is a rotor? This mechanism is a component that enables devices of different types and characteristics to function. From electric motors to helicopters to wind turbines, this component contributes to the operation of many devices. The area in which it is used changes the way it works and the technical characteristics of the product. For example, in electric generators, a magnetic field is created by rotating the rotor. This rotational movement creates an electromagnetic induction in the stator, generating electrical energy.
The design and working principle of these products differ for each application. In order to understand how to use the rotor for a specific device or system, it is recommended to consult the user manual of the relevant equipment.
The Rotor What Does it Mean?
The rotor, a functional part of an electrical device or machine, usually provides the rotating motion that makes the operation of the device possible. This motion is either used directly as mechanical energy or plays an important role in energy conversion. In electric motors, the magnetic interaction that causes the rotor to rotate forms the basis of the device’s operating principle.
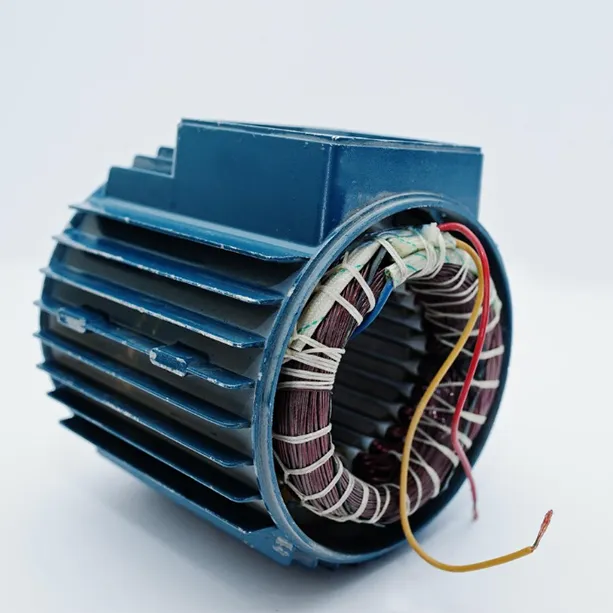
Motor Rotor and Types
The motor rotor is perhaps the first type of rotor that comes to mind. The rotor, one of the basic components of electric motors, together with the fixed component called the stator, provides the movement and energy conversion of the motor.
A common type of rotor in electric motors is the squirrel cage rotor. This type of rotor takes its name from the fact that its windings resemble the shape of a squirrel cage. Squirrel cage rotors are commonly used in induction motors. This type of rotor can show a slip cycle change with increasing speed of the motor.
However, there is also another type of rotor available, called a wound rotor. This type of rotor may be more suitable for certain applications. Its windings are designed to optimize energy transfer and conversion.
Squirrel-cage rotors are named after their aluminum or copper windings, which are cast in a similar shape to the surface of the rotor. In wound rotors, the rotor windings are energized from an external power source. Both types are commonly used in induction motors.
Critical Role and Applications of the Rotor
Rotors are not limited to electric motors. You can also find other mechanical devices. For example, in a helicopter, the main rotor allows the vehicle to rise and move through the air. Likewise, rotors in wind turbines are designed to convert wind energy into mechanical energy.
In general, a rotor is a component that has a key role in the conversion of energy from one form to another. This conversion can form the basis for movement, heat generation or the storage of energy in another form.
The rotor plays a critical role in both simple and complex machines. From electric motors to helicopters, wind turbines to industrial equipment, rotors are indispensable to the functioning of the modern world. The rotational motion of these components is essential for energy conversion, motion transfer and other mechanical functions. Therefore, the design, manufacture and maintenance of rotors is vital at every stage of technological progress.

What Are Rotor Types?
Rotors are crucial components in electrical machines such as motors and generators, responsible for converting electrical energy into mechanical energy and vice versa. Understanding the different types of rotors is crucial for choosing the right motor or generator for specific applications. Here are the various types of rotors in general, focusing on their structure, functionality and application:
The squirrel cage rotor is the most common type of rotor used in electric motors, especially induction motors. It consists of a laminated magnetic core with copper or aluminum rods inserted into slots, which are then short-circuited by end rings. This design creates a structure that resembles a squirrel cage, hence the name.
The salient pole rotor is typically used in low speed applications such as hydroelectric generators. This type of rotor has large, protruding poles (salient poles) mounted on the rotor shaft. The poles are usually equipped with rotor windings and may use slip rings for external connections.
In some advanced high-speed motors and generators, a rotating magnetic rotor design is used. This involves placing permanent magnets inside the rotor to create a constant magnetic field.
Each rotor type has specific applications based on its design and functionality. When selecting a rotor, it is essential to consider factors like the speed of operation, the nature of the load, and the desired efficiency.
Understanding these rotor types and their unique characteristics helps in choosing the right motor or generator for your needs, ensuring optimal performance and efficiency.
What is a Rotor and What Does It Do?
A rotor is one of the fundamental components of electric motors and generators, and it functions as the rotating part of the machine.
Broadly defined, a rotor is a system used in electric motors and generators to convert mechanical energy into electrical energy. The rotor rotates around a fixed part called the stator, and together, these two parts enable the motor to operate.
The working principle of a rotor is related to the formation of a magnetic field.
In electric motors, the electric current passing through the stator windings creates a magnetic field. This field acts on the conductors on the rotor, causing it to rotate.
The stator remains stationary and supports the rotor’s rotation by providing the magnetic field. This is how energy is produced, and the motor operates.
The working principle of the rotor is as follows: it is based on electromagnetic induction. The rotating magnetic field created by the stator exerts a force on the conductors on the rotor, causing it to rotate. However, the rotor’s speed typically cannot match the speed of the stator’s magnetic field. This speed difference is called slip, and in asynchronous motors, the rotor operates due to slip.
In general, the working principle is that rotors are the rotating components of electric motors and generators, and they operate under the influence of a magnetic field.
Rotors are widely used in various industrial fields, particularly in industry and technology. They are essential components in many machines such as electric motors rotors, fans, pumps, and conveyor systems.
In industrial settings, they are used to ensure the operation of motors and play a crucial role in energy conversion in various machines and devices.
